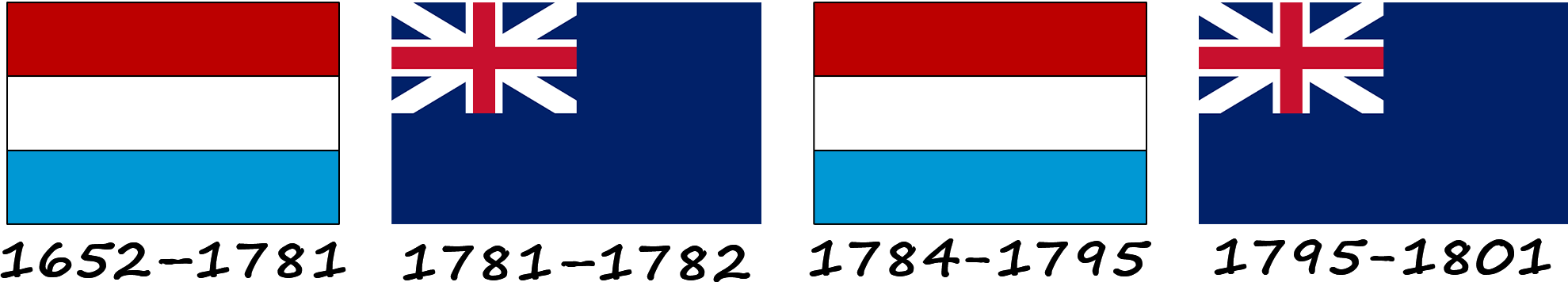
Around 1498, European settlers encountered the Guyanese lands, which had previously been inhabited by Arawaks and Caribs. The first colonists were Dutch, so their flags had Dutch symbols. The first colony was Essequibo, founded in 1616. Later, two more colonies appeared: Berbice in 1627 and Demerara in 1773. These colonies were governed by the Dutch West India Company, which had its own flag with red, white, and blue colors. Later, British emigrants from other Caribbean colonies were also allowed to enter Guyana, and Demerara became the main place of their settlement. In 1781, the Dutch colonies were captured by the British.
For many years, Guyana experienced conflicts and changes of power on its territory. In 1804, British sovereignty over the colonies was increasing, leading to a desire to expand its influence over the Essequibo River, which belonged to Venezuela. In 1835, the border between British Guiana and Venezuela was established along the Orinoco River. Part of the territory of Venezuela was occupied by the British, and units of their army continue to claim this territory today. British colonial flags appeared in Guyana in 1875.
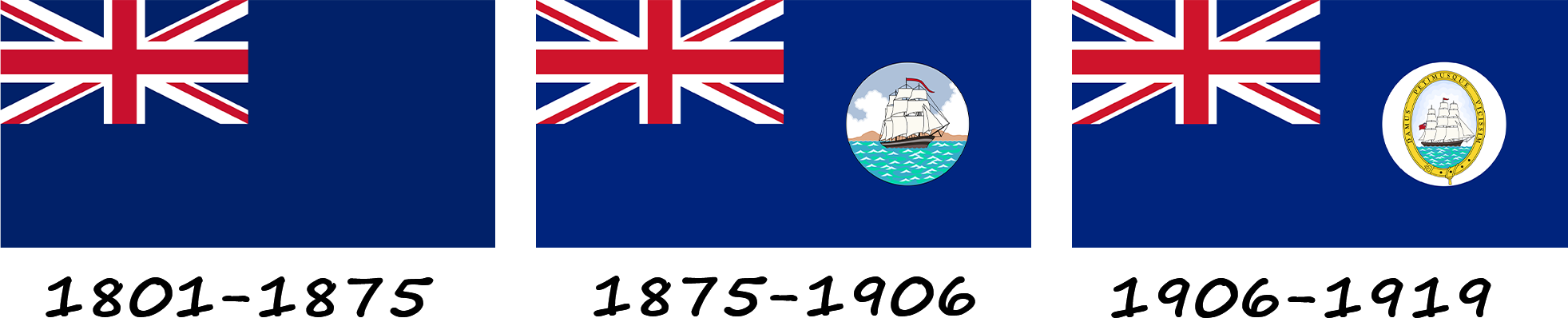
The colony's flag, which was used until 1906, had a dark blue background with the Union Jack in the corner and the colonial coat of arms on the right. The coat of arms was rounded and depicted a ship with sails sailing on a sea of waves. In 1906, the first modification of the flag took place, as a result of which the brown mountains in the background were removed and the sky became blue and white. The coat of arms became oval with the golden-yellow inscription "Give and receive in return". In 1919, it was decided to remove the white circle around the coat of arms and place it directly on the blue background of the flag.

After the political changes in 1955, a round circle with the coat of arms in the center appeared on the flag, reflecting the independence of the colony. The design of the ship changed, the number of sails decreased, and the color of the ship became golden brown. The yellow ribbon with the colony's motto was replaced with a new Guyana flag. The independence movement was gaining momentum, and the idea of a free Guyana was spreading. In 1960, American vexillologist Whitney Smith developed a new design for the Guyana flag. The new flag of Guyana won the competition, but it took several years to adopt the flag and gain independence. The Government of Guyana invited Whitney Smith to celebrate Independence Day in Georgetown.
Guyana's flag was officially adopted in 1966 and has not changed since then. It consists of a green rectangle with a yellow triangle on the left side of the flag. On the yellow triangle is a red equilateral triangle with a black outline. The two triangles share a common base, but their vertices do not coincide. The flag of Guyana represents the national identity of the country and symbolizes the freedom and autonomy granted by the government.








